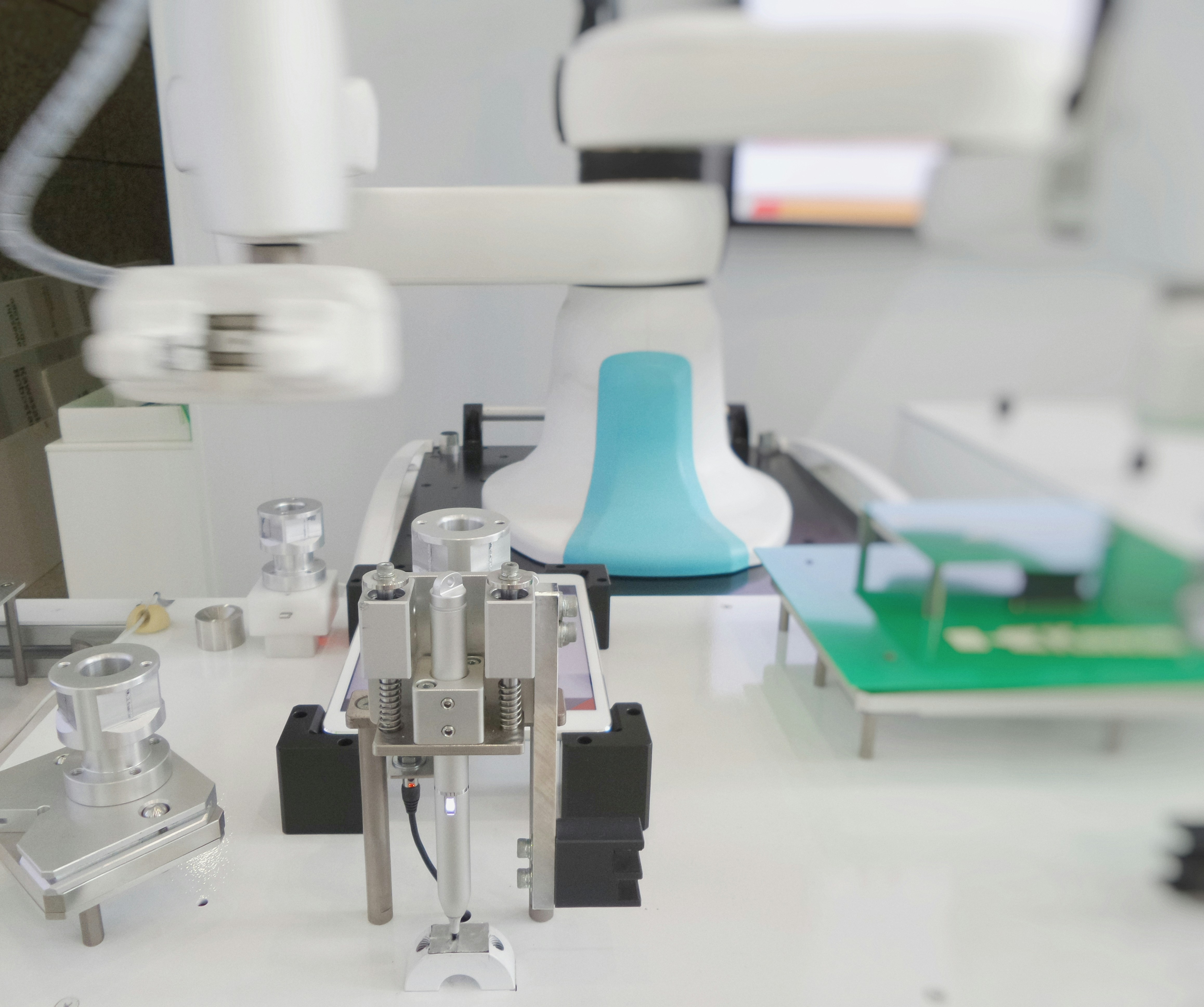
Technology
Automation and the Future of Employment: Amazon’s Move to Replace 600,000 Workers with Robots
Introduction: The Shift Towards Automation
The rapid evolution of technology has ushered in an era where automation plays an increasingly prominent role in the labor market. In particular, recent revelations regarding Amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots, saving only 30 cents on each delivery’, as disclosed in leaked documents, highlight a significant trend impacting employment across various sectors. This shift raises vital questions about the future of human jobs and the role of robots in the workplace. How will this automation affect those currently employed, and what industries might see similar changes?
As companies strive to enhance efficiency and cut costs, the adoption of robots in the workplace, exemplified by Amazon’s initiatives, presents both challenges and opportunities. These advances in automation facilitate substantial operational improvements, allowing businesses to process orders faster and with fewer errors. However, this efficiency often comes at the cost of human employment, prompting concerns about the potential for widespread job displacement as automation takes jobs traditionally held by humans.
In light of these developments, it is essential for employees and job seekers to understand how to benefit from automation. As automation becomes more integrated into business practices, individuals may need to re-evaluate their skills and consider diversifying their qualifications to stay relevant in an ever-evolving job market. Workers must be proactive in their approach to career development, identifying areas where they can adapt and thrive amidst these technological advancements.
As we navigate through this transformative period, it is crucial to consider the long-term implications of automation on employment. Will the integration of robotics create new job opportunities, or will it predominantly serve to eliminate positions? In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the potential impact of automation and offer insights on how individuals can prepare for the changes ahead.
Understanding Amazon’s Automation Plan
Recent revelations from leaked documents have shed light on Amazon’s strategic initiative to replace 600,000 workers with robots, a move that has sparked significant debate in the workforce and technology communities. The company aims to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs through automation, with the projected savings estimated at a mere 30 cents per delivery. This financial incentive appears to drive the push for integrating robotics into various facets of Amazon’s logistics and fulfillment operations.
The motivation behind Amazon’s shift towards automation is multifaceted. First and foremost, the adoption of robots in the workplace can potentially streamline processes, allowing the company to manage an increased volume of orders with reduced reliance on human labor. This aspect of automation facilitates faster delivery times and greater inventory management, positioning Amazon to maintain its competitive edge in the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape. Furthermore, there is a growing trend among corporations to leverage technology as a means to address labor shortages and rising operational costs, underscoring why automation takes jobs.
However, as employers increasingly turn to robots, this raises critical questions about the future of employment. Many workers are left questioning their job security in light of automation’s trajectory. While some fear the loss of jobs, others are encouraged to think about how to benefit from automation by acquiring new skills suited for a more technology-driven workplace. Upskilling and adapting to evolving work environments are paramount for employees who wish to remain relevant in the job market over the next decade.
In conclusion, understanding the implications of Amazon’s plans in leveraging robots highlights the broader picture of workplace automation, prompting a critical assessment of both the financial motives and the socioeconomic consequences of these transformative changes in the work environment.
The Human Cost of Automation
The surge of automation, especially highlighted by Amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots’ saving only 30 cents on each delivery revealed in leaked documents, has raised significant concerns regarding the future of employment. The promise of increased efficiency through robots in the workplace comes with a profound human cost, notably job displacement and insecurity among workers. As companies embrace automation, particularly in sectors heavily dependent on wage labor, the socio-economic landscape faces alterations that extend far beyond financial metrics.
The immediate effect of implementing such aggressive automation strategies includes the potential job losses that can destabilize entire communities, particularly those reliant on the income generated from these positions. The disruption of stability in the workforce can lead to psychological distress among displaced workers, manifesting as anxiety and diminished self-worth. Studies have shown that individuals faced with sudden unemployment due to automation often grapple with feelings of isolation and uncertainty about their future.
Beyond individual repercussions, the broader implications for the workforce and society cannot be overlooked. As robots enter roles traditionally filled by humans, the demand for low-skill labor diminishes, compounding the existing economic inequalities. Those who may find it challenging to pivot to new industries may become marginalized, leading to increased reliance on social support systems. Furthermore, this shift raises essential questions about how to benefit from automation while safeguarding the interests of those adversely impacted. Society must consider comprehensive strategies to equip workers with relevant skills and opportunities for growth, ensuring that the transition into an automated future does not come at the expense of human dignity.
Addressing the challenges presented by automation requires a proactive approach aimed at resilience. Initiatives focusing on retraining and upskilling can empower workers in adapting to an evolving job market, ultimately rendering them more skilled and versatile. Understanding what to do to keep a job over the next ten years becomes essential in navigating the complexities introduced by automation. In this way, while benefits of technology continue to emerge, the human costs must be critically assessed and addressed.
Jobs at Risk: 20 Positions Eliminated by Automation
As automation continues to advance, a number of traditional jobs are being increasingly replaced by technology. The advent of robots in your workplace has significantly altered the employment landscape, with companies focusing on methods to streamline operations and reduce costs. Amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots, saving only 30 cents on each delivery revealed in leaked docs’ illustrates how serious this trend has become. Below are 20 positions that have been heavily impacted by these technological shifts.
1. **Retail Cashiers**: The rise of self-checkout systems has dramatically reduced the need for human cashiers.
2. **Manufacturing Workers**: Automation in assembly lines, often involving robots, has led to significant job losses in this sector.
3. **Warehouse Staff**: Companies are leveraging robotics to manage inventory, leading to fewer manual labor roles.
4. **Data Entry Clerks**: Software solutions can complete tasks requiring data input more efficiently than humans.
5. **Travel Agents**: Online booking platforms have diminished the need for traditional travel advisory roles.
6. **Telemarketers**: Automated calling systems and artificial intelligence (AI) have greatly reduced human involvement in this role.
7. **Farm Workers**: Agricultural automation, including robotic machinery, has decreased the demand for manual farm labor.
8. **Customer Service Representatives**: AI chatbots now handle numerous customer inquiries, leading to fewer positions in this area.
9. **Bank Tellers**: The increasing reliance on online and mobile banking has made many teller roles obsolete.
10. **Post Office Workers**: Sorting and delivery processes are being automated, resulting in fewer employment opportunities.
11. **Fast Food Workers**: Self-service kiosks and automated cooking systems are taking over various roles in fast food establishments.
12. **Construction Workers**: Advancements in machinery mean less manual labor is required on construction sites.
13. **Inventory Clerks**: Automation in stock management reduces the necessity for manual inventory tracking.
14. **Security Patrols**: Surveillance technology is increasingly replacing on-foot security personnel.
15. **Librarians**: Digital resources and automated cataloging systems have lessened the demand for traditional library roles.
16. **Newspaper Reporters**: Automated journalism tools are capable of producing news content, impacting jobs in this domain.
17. **Unix or Linux System Administrators**: Automated management tools can perform many routine IT tasks, reducing the need for human oversight.
18. **Video Editors**: AI-driven editing software has started to replace certain aspects of the editing process.
19. **Insurance Underwriters**: Algorithms now assess risks, reducing demand for human underwriters.
20. **Research Analysts**: AI can gather and analyze data, thereby minimizing the need for human analysts in many fields.
Overall, the trend of automation takes jobs is reshaping the workforce, compelling individuals to adapt to the new reality of work. As automation continues to integrate into various sectors, understanding how to benefit from automation while retaining job security becomes paramount. By evolving skill sets and embracing change, workers can better position themselves for success over the next ten years.
Top 5 Companies Leading the Automation Revolution
The automation revolution is rapidly redefining the employment landscape, with many companies investing heavily in technologies designed to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. Among the leaders in this transformative movement are several notable companies that manufacture and sell automation tools, systems, and robots. The following five companies are at the forefront of this trend, contributing significantly to the shift towards mechanization.
First, Amazon stands out as a major player not just in retail but in automation technologies as well. Particularly with the news about Amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots’ saving only 30 cents on each delivery revealed in leaked docs, the company illustrates the dramatic impact automation can have on its workforce. Amazon’s investments in robotics are designed to streamline operations, reduce operational costs, and ultimately improve customer experience.
Second, Walmart has embraced automation through self-checkout systems, developed in collaboration with various tech partners. These innovations not only improve checkout speeds but also significantly reduce the number of cashiers required, demonstrating how automation takes jobs previously done by humans while catering to consumer demand for efficiency.
Third, Boston Dynamics has gained attention for its sophisticated robotic solutions. The company’s creations, such as Stretch, are designed to optimize warehouse operations, showcasing the potential of robots in industrial settings. The integration of such technologies into the workplace prompts businesses to consider how to benefit from automation, ultimately altering labor dynamics.
Fourth, Siemens is a leader in industrial automation, providing cutting-edge solutions tailored for manufacturing sectors. Their advanced robotics and automation systems highlight the capabilities of robots in improving productivity while addressing the challenges of a shrinking workforce.
Lastly, UiPath specializes in robotic process automation (RPA), offering software solutions that automate routine tasks across various industries. This positions UiPath as a key player in helping organizations adopt automation effectively, emphasizing the necessity of adapting skills to thrive in an evolving job market. As companies like these evolve, it becomes increasingly important for workers to consider what to do to keep a job over the next ten years, as adapting and integrating into this new technological landscape will be essential.
Embracing Change: The Need for Investment in Automation Tools
As the landscape of employment continues to evolve, particularly with developments such as amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots’ saving only 30 cents on each delivery revealed in leaked docs, it is crucial for businesses and individuals to acknowledge the necessity of investing in automation tools. The gradual shift toward automation is not merely a temporary trend; it is a profound transformation that necessitates proactive adaptation to maintain competitiveness in an increasingly dynamic job market. By embracing automation, organizations can streamline their processes, enhance productivity, and remain resilient against economic fluctuations.
Automation tools come in various forms, including software solutions, artificial intelligence systems, and robotic technologies. Each category offers distinct advantages that can optimize labor and reduce errors. For instance, AI-driven software can analyze data faster than any human, aiding in decision-making processes, while robotic systems can perform repetitive tasks with exceptional precision. This integration of technology into daily operations allows businesses to allocate human resources to more strategic roles, thereby driving innovation and growth.
Moreover, the benefits of investing in automation extend beyond mere efficiency gains. Companies that adopt these tools can navigate labor shortages more effectively, ensuring they meet customer demands without a significant increase in operational costs. This capability is especially critical in sectors where turnover rates are high or where specialized skills are necessary. Understanding how to benefit from automation can provide employees with a significant advantage, including opportunities to upskill and transition into roles that require advanced technological competencies.
As we move further into the age of automation, it is essential for individuals to consider what to do to keep a job over the next ten years. This includes upskilling in areas where human expertise complements automation. In conclusion, investing in automation tools is not just a business imperative; it is a critical step toward preparing for and thriving in the future employment landscape.
The Future of Work: Transitioning from Labor to Tool Leverage
As businesses increasingly adopt automated processes, the future of work is poised to evolve dramatically. The concept of leveraging tools rather than relying solely on human labor is gaining traction, particularly in light of Amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots’, saving only 30 cents on each delivery as revealed in leaked documents. This shift in strategy prompts a reevaluation of how labor is defined and the role of automation in modern workplaces.
By utilizing advanced technology and robotic systems, companies can enhance productivity while minimizing costs associated with human labor. Automation enables organizations to streamline processes and create new efficiencies, but it also necessitates a transition in the workforce landscape. As jobs traditionally filled by humans become increasingly automated, there lies a unique opportunity for individuals and businesses to adapt by leasing tools and automation systems to others. This approach can cultivate a new business model focused on efficiency and adaptability, ensuring sustainability in an ever-evolving economic environment.
The benefits of embracing this mindset are manifold. For instance, companies that adopt robotics not only reduce operational costs but also increase output quality and speed. It allows for a more dynamic adaptation to market demands. Additionally, workers can transition into new roles that prioritize managing and maintaining these automated systems, thus ensuring their relevance in a landscape where automation takes jobs previously held by humans.
In this rapidly changing landscape, it becomes essential for individuals to identify ways to benefit from automation. Understanding how to leverage technology effectively can provide a competitive edge. Moreover, gaining skills in areas complementary to automation, such as system optimization and data analysis, is crucial for maintaining employability over the next ten years. The emphasis on collaborative engagement with automation sets a foundation for future workers to thrive in increasingly technologically advanced workplaces.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Automation
The rise of automation has prompted many businesses to integrate advanced technologies into their operations, ultimately reshaping the workforce landscape. Several companies have successfully adopted automation strategies that can serve as valuable examples for others contemplating similar transitions. One prominent case is that of Amazon itself. The company’s decision, as indicated in the recent reports about Amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots’, exemplifies the growing trend towards increased automation in logistics and distribution. This controversial move emphasizes cost savings, with projected reductions of 30 cents on each delivery. While such changes can trigger concerns regarding job displacement, they also underscore the efficiency that robots in your workplace can bring to operations.
Another remarkable case can be observed in the manufacturing sector, particularly with automotive giants like Ford and Tesla. Both firms have leveraged robotics to enhance production lines, resulting in accelerated output and consistent quality control. Automation has permitted these companies to streamline processes and reduce time and costs associated with traditional assembly methods. The success of this transition reveals the potential of automation to not only improve operational efficiency but also to foster innovation within firms.
Moreover, in the realm of customer service, organizations like Domino’s Pizza have integrated AI-driven chatbots to facilitate order placements and customer inquiries. By automating these functions, they have not only improved customer satisfaction but also allowed human employees to focus on more complex tasks requiring personal attention. These case studies illustrate the dual aspects of automation taking jobs while concurrently offering solutions on how to benefit from automation. Businesses that learn from these examples can develop strategies to sustain employment while embracing technological advancements. Companies must also consider training and development programs to equip their workforce for new roles that may emerge following automation implementation.
Conclusion: Preparing for an Automated Future
The transition towards automation, highlighted by amazon’s plot to ‘replace 600,000 workers with robots’ saving only 30 cents on each delivery revealed in leaked docs, underscores a significant shift in the labor market. As this technology continues to evolve, it is critical for employees and job seekers alike to understand the implications of such changes on their careers and job security. Automation takes jobs, and while AI news frequently discusses the advancements in robotics, particularly in workplaces like Amazon’s, it is essential to recognize that these innovations should not incite fear but rather inspire proactive strategies.
Preparing for an automated future necessitates a change in mindset. Workers must consider how to benefit from automation rather than resist it. This may involve pursuing skill development, learning new technologies, and adapting to new roles that emerge as a result of these advancements. Engaging in lifelong learning and seeking training opportunities can position individuals favorably in a workforce that increasingly relies on robots and AI. Those who are equipped with the right skills will be more likely to survive—and thrive—amidst these changes.
Furthermore, examining the types of jobs that are less likely to be automated is crucial. While many repetitive tasks are at risk of being supplanted by machines, roles that emphasize human interaction, creativity, and complex problem-solving may remain in demand. Employees should contemplate their current positions and consider how they can evolve to align their roles with emerging industry needs over the next ten years.
Overall, adapting to the evolving job landscape is essential. Individuals who remain flexible and forward-thinking will position themselves effectively in a world increasingly influenced by automation and robotics.